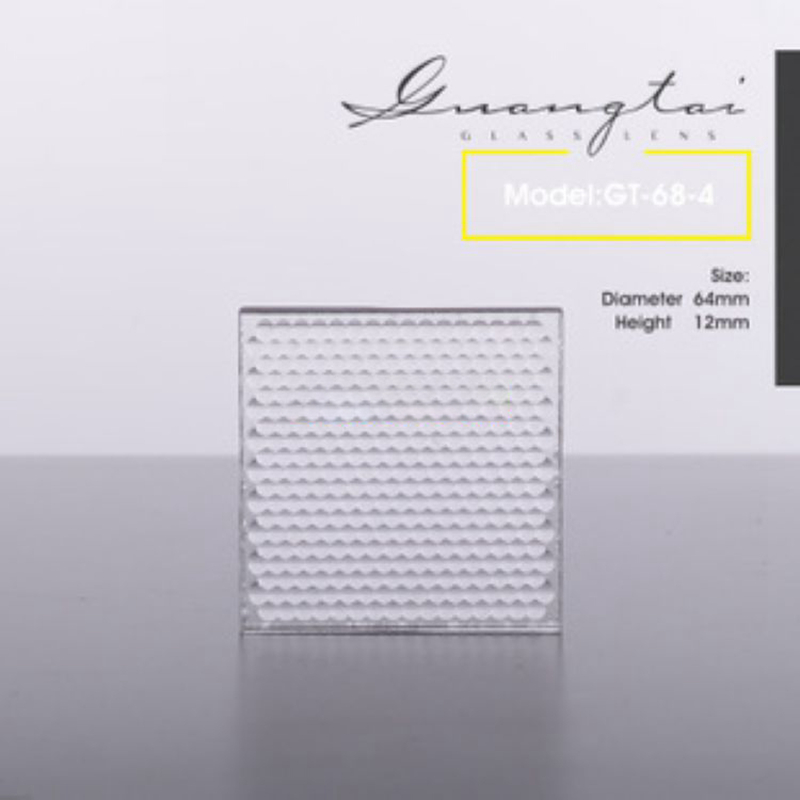
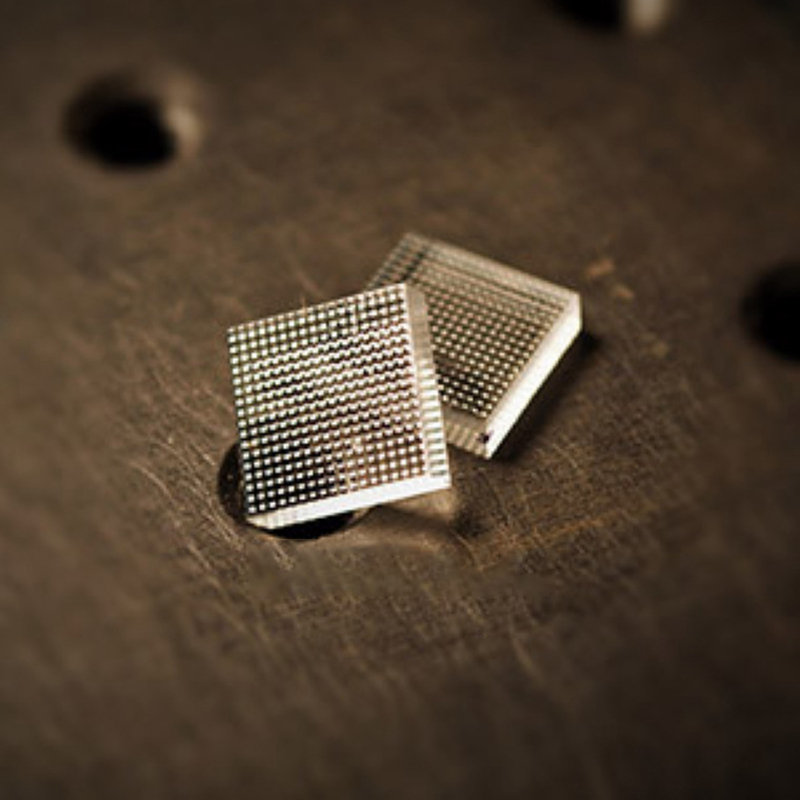
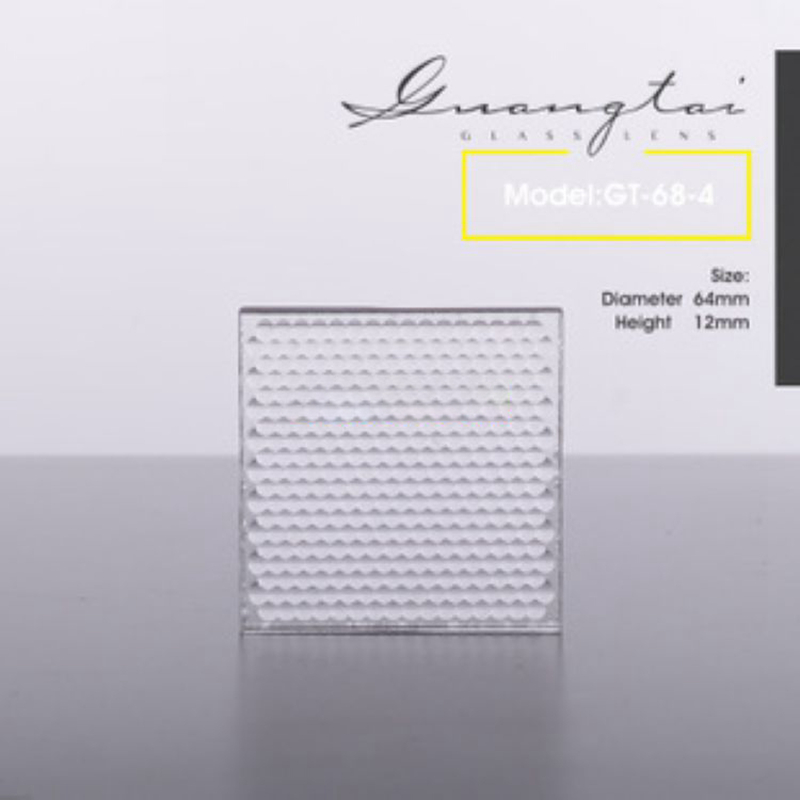
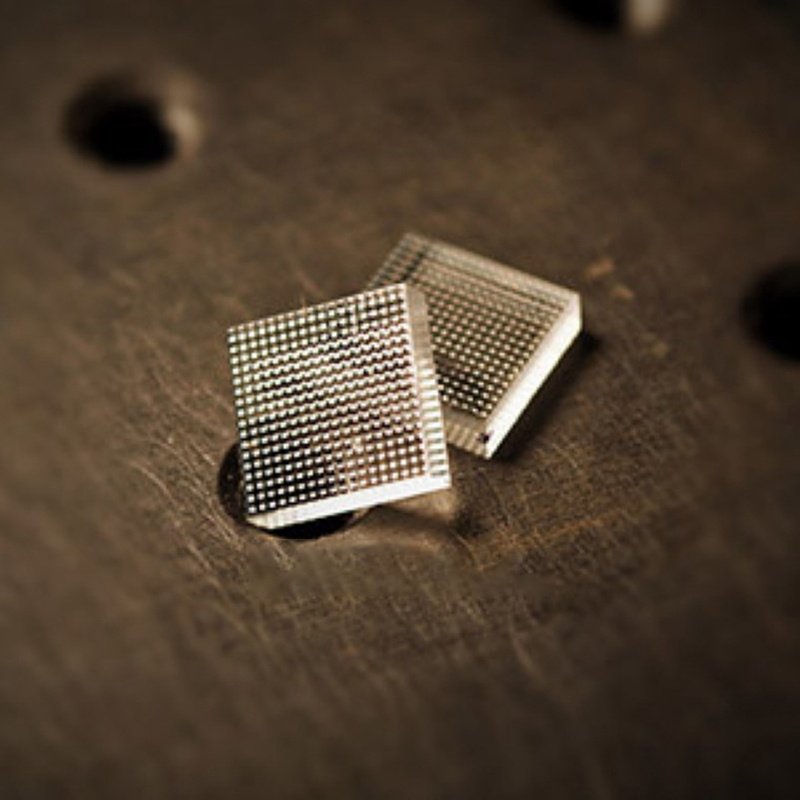
Description
Micro Lens Z Array,EdmundMicrolens Replacement Model,ImitationThorlabsMicrolens, ReplacementTHorlabsThe Micro-Lens
Domestic Microlens Company, Chinese Microlens Manufacturer, Glass Microlens, Professional Design Microlens, Customized Microlens, Shi Ying Microlens
As International Giants Such as Apple and TSMC Put Resources into the Field of Optical Micro-Processing,WLO(Wafer-Level Optical Components),DOE(Diffraction Optical Element) and Microlens (Micro lens arrays) in the past Two Years, It Has Risen Rapidly, in Hartman–Shack Wave Front Sensor, Depth Camera, Optical Fiber Communication and Other Fields.
Currently, Microlenses on the Market Mainly IncludeSUSS,Thorlabs(Solebo),Edmund(Aitmont) and Wilks Optoelectronics, Among Which Standard Models Are Mainly ProvidedThorlabs,Edmundand Wilks Optoelectronics. As a Major Manufacturer of Micro-Optical Components in China, Wilks Optoelectronics Provides Cycle30um~1000umThe Micro-Lens Nearly50There Are More Standard Models than the Other Two Models Mentioned above. In Terms of Quality, Our Surface Shape Accuracy and Error Are Not Inferior to Imported Similar Products, While the Price Is Obviously Reduced, Which Is an Option to Replace Imported Similar Products.
Hartmann–The Shack (Shack-Hartmann) Wave Front Sensor Is One of the Main Applications of Microlens, and Microlens Array Is Usually Placed inCCDa Specific Position in Front of the Array, So ThatCCDThe Plane Wave Front Imaging on the Sensor Will Form a Regular Bright Spot Pattern. However, If inCCDThe Imaging Light on the Sensor Will Be Composed of Spots with Certain Intervals Including Deviated Spots and Disappeared Spots, Which Indicates That the Wave Front Is Distorted. This Information Can Calculate the Wave Front Shape Incident to the Microlens Array. Hartmann–Shaker Wave Front Sensor Can Be Used to Represent the Performance of Optical System, and Can Also Be Used to Control Adaptive Optical Elements by Real-Time Monitoring Wave to Achieve the Purpose of Eliminating Wave Front Distortion before Imaging.
The Connection and Coupling between Optical Fiber and Optical Fiber Is Another Potential Application Direction. Good Microlens Design Can Improve Coupling Efficiency and Optimize Coupling Structure, at Present, We Have Been Able to Provide All-in-One Optical Fiber Communication Coupling Microlens.
Characteristics of Microlens
Size Is Generally10 mm x 10 mmandThorlabs,EdmundSame, Users Can Transfer1Inch Frame
Standard Products Are Not Coated, and Can Be Coated According to User Needs.
Fused Silica Substrate
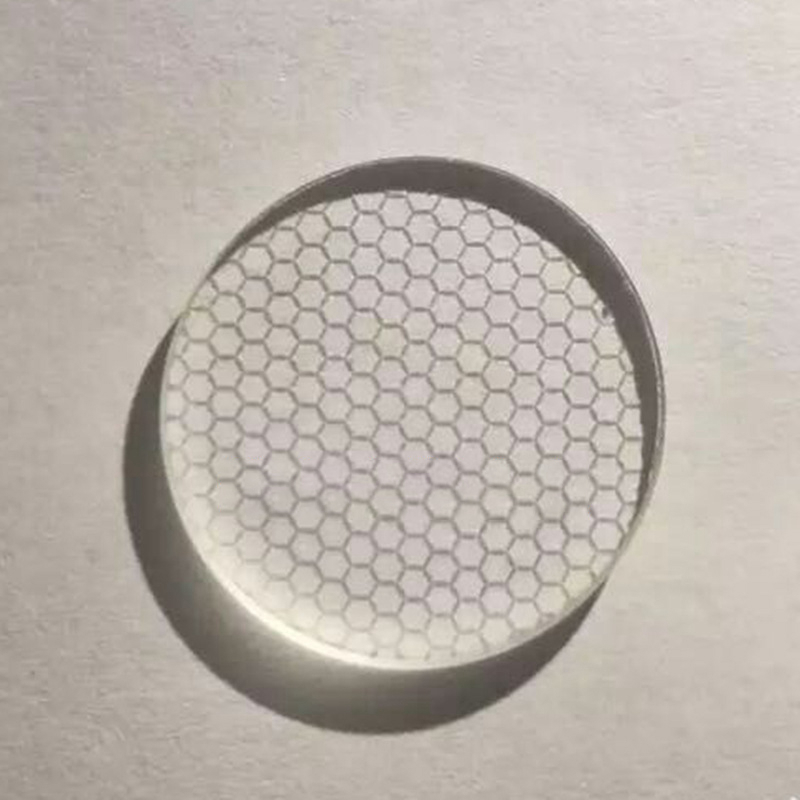
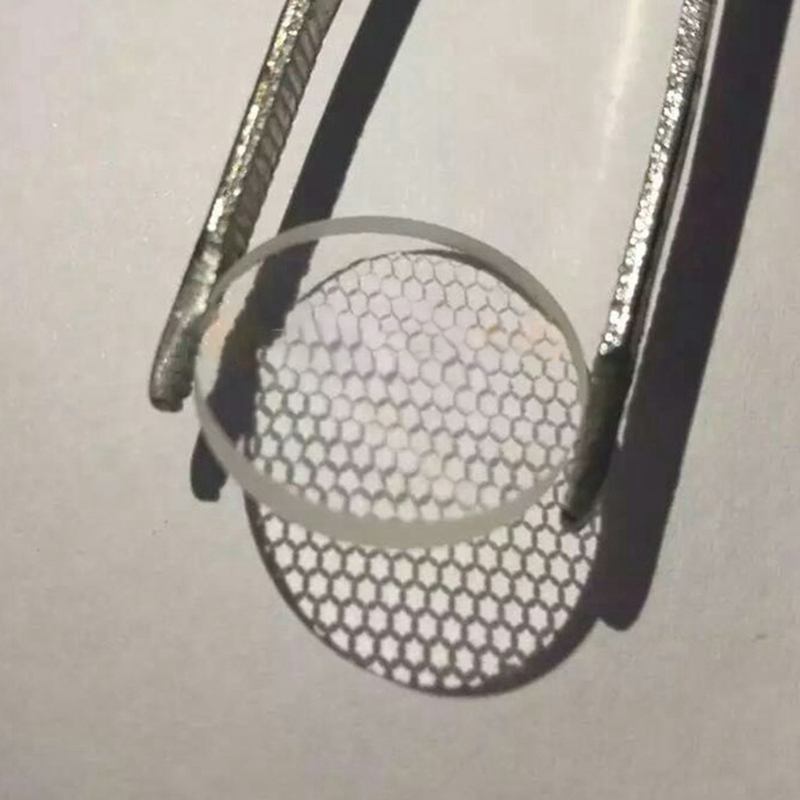
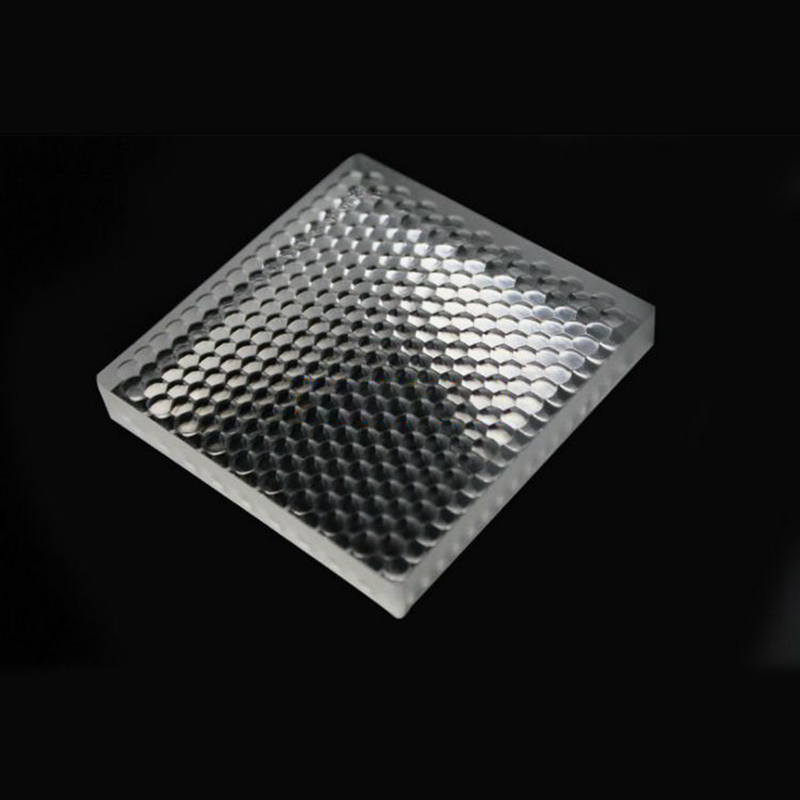
Microlenses Are Arranged by Square Grid and Hexagonal Grid
Lens Array Cycle50um~1000um, There Are More than Ten Choices
Spot Size near Diffraction Limit
High Light Spot and Background Contrast
The Attractiveness of Electro-OpticalMLSeries Microlens Arrays Have Good Transmission Characteristics from Ultraviolet to Infrared Due to the Use of Fused Shi Ying Materials, Making Them Ideal for Many Applications. Microlens Has a Planoconvex Shape, Whose Appearance Is round, and the Bottom Surface Is Usually Square, Which Is Arranged According to Square, and There Are Also Standards of Hexagonal Microlens Arranged According to Hexagon. The Maximum Filling Coefficient of Microlens Can Reach100%.
The Microlens Provided by Vilks Optoelectronics Is Processed Based on the Photoetching Technology in Semiconductor Processing Technology, Which Makes the Shape and Position of Each Microlens Have Good Consistency. The Optical Effect Is Better than the Microlens Array Produced by Molded Epoxy Resin, and the Resulting Spot Size Can Approach the Diffraction Limit.
Naming Rules for Microlens Arrays:
ML- (Sub-Unit Shape)-(Sub-Unit Size)-F(The Focal Length)
ML: Micro Lens
Spread Geometry/Subunit Shape:SSquare,HHexagon
Subunit Size: Unit Μm
Focal Length: Unitmm
For Example:ML-S32-F0.08For a Square32×32μmSubunits Are Arranged in Square, Focal Length0.08mmThe Micro-Lens Array
ThorlabsMicro Lens Naming:MLA-Sub-Unit Size–The Focal Length–The Coating of a Cycle150~300um
ThorlabsMicrolens Model:MLA150-5C,MLA150-7AR,MLA300-14AR
EdmundMicro Lens Naming: Model Has No Actual Meaning, Micro Lens Period300~500um
EdmundMicrolens Model:#64-478,#64-477,#64-476,#64-483,#64-482,#64-480,#64-488,#64-479,#84-132,#64-489,#64-490,#83-910,#86-745
Standard Specification of Microlens Array:
- 1. Square Microlens, Square Cycle
|
The Micro-Lens Model |
Sub-Unit Shape |
Subunit Size (Period) |
The Focal Length |
Lens Dimensions |
The Center Wavelength |
|
ML-S32-F0.08 |
Square |
32μm |
0.08mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S32-F0.16 |
Square |
32μm |
0.16mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S50-F0.3 |
Square |
50μm |
0.3mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S64-F0.45 |
Square |
64μm |
0.45mm |
12×12mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S75-F0.75 |
Square |
75μm |
0.75mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S100-F0.5 |
Square |
100μm |
0.5mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S100-F1 |
Square |
100μm |
1mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S100-F3 |
Square |
100μm |
3mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S108-F3 |
Square |
108μm |
3mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S120-F2.4 |
Square |
120μm |
2.4mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S150-F3 |
Square |
150μm |
3.0mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S200-F7.9 |
Square |
200μm |
7.9mm |
8×8mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S237-F7 |
Square |
237μm |
7mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S250-F5 |
Square |
250μm |
5mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S250-F5 |
Square |
250μm |
5mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S250-F10 |
Square |
250μm |
10mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S300-F5 |
Square |
300μm |
5mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S300-F5 |
Square |
300μm |
5mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S300-F10 |
Square |
300μm |
10mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S300-F30 |
Square |
300μm |
30mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S310-F10 |
Square |
310μm |
10mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S310-F10 |
Square |
310μm |
10mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S310-F7 |
Square |
310μm |
7mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S310-F7 |
Square |
310μm |
7mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S500-F15 |
Square |
500μm |
15mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S500-F30 |
Square |
500μm |
30mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S500-F30 |
Square |
500μm |
30mm |
12×12mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S500-F35 |
Square |
500μm |
35mm |
12×12mm |
1550nm |
|
ML-S500-F50 |
Square |
500μm |
50mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S550-F35 |
Square |
550μm |
35mm |
12×12mm |
1550nm |
|
ML-S600-F25 |
Square |
600μm |
25mm |
10×10mm |
633nm |
|
ML-S1000-F30 |
Square |
1000μm |
30mm |
12×12mm |
1550nm |
|
ML-S1000-F35 |
Square |
1000μm |
35mm |
12×12mm |
1550nm |
|
ML-S1015-F61 |
Square |
1015μm |
61mm |
10×10mm |
650nm |
|
ML-S1015-F153 |
Square |
1015μm |
153mm |
10×10mm |
650nm |
|
ML-S1100-F153 |
Square |
1100μm |
153mm |
10×10mm |
650nm |
|
ML-S1500-F153 |
Square |
1500μm |
153mm |
10×10mm |
650nm |
- 2. Hexagonal Microlens, Hexagonal Period
|
The Micro-Lens Model |
Sub-Unit Shape |
Subunit Size (Period) |
The Focal Length |
Lens Dimensions |
The Center Wavelength |
|
ML-H1000-F30 |
Hexagon |
1000μm |
30mm |
Φ16mm×2 |
450nm-2800nm |
|
ML-H1000-F40 |
Hexagon |
1000μm |
40mm |
Φ16mm×2 |
450nm-2800nm |
|
ML-H1000-F50 |
Hexagon |
1000μm |
50mm |
Φ16mm×2 |
450nm-2800nm |