Lasers can broadly be divided into 3 major types: Solid-state, Gas, and Liquid.
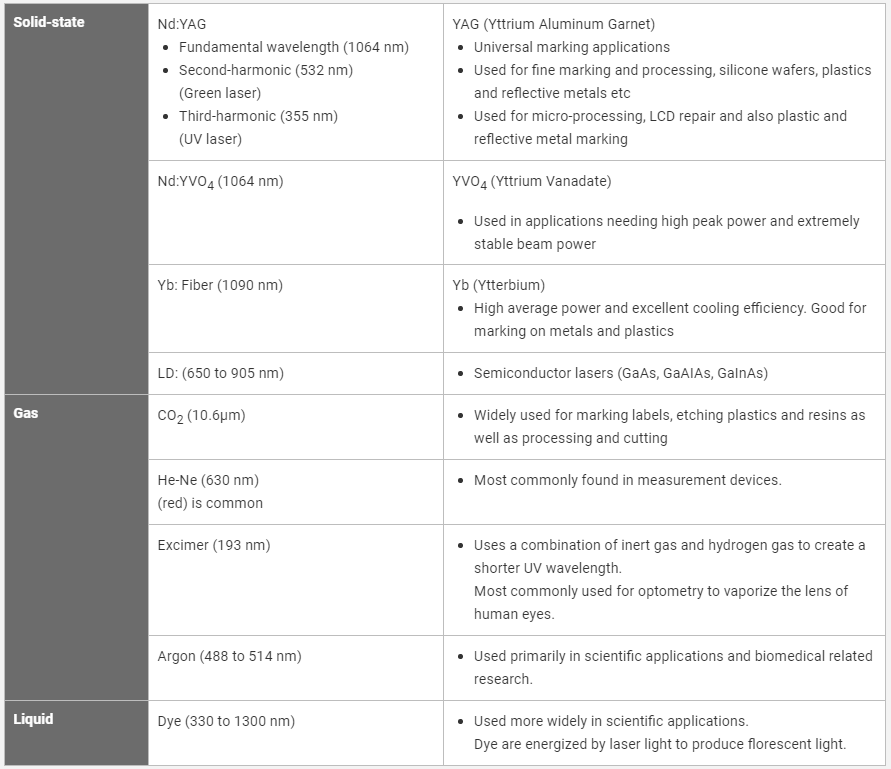
Solid-state
Nd:YAG
Fundamental wavelength (1064 nm)
Second-harmonic (532 nm)
(Green laser)
Third-harmonic (355 nm)
(UV laser)
YAG (Yttrium Aluminum Garnet)
Universal marking applications
Used for fine marking and processing, silicone wafers, plastics and reflective metals etc
Used for micro-processing, LCD repair and also plastic and reflective metal marking
Nd:YVO4 (1064 nm)
YVO4 (Yttrium Vanadate)
Used in applications needing high peak power and extremely stable beam power
Yb: Fiber (1090 nm)
Yb (Ytterbium)
High average power and excellent cooling efficiency. Good for marking on metals and plastics
LD: (650 to 905 nm)
Semiconductor lasers (GaAs, GaAIAs, GaInAs)
Gas
CO2 (10.6μm)
Widely used for marking labels, etching plastics and resins as well as processing and cutting
He-Ne (630 nm)
(red) is common
Most commonly found in measurement devices.
Excimer (193 nm)
Uses a combination of inert gas and hydrogen gas to create a shorter UV wavelength.
Most commonly used for optometry to vaporize the lens of human eyes.
Argon (488 to 514 nm)
Used primarily in scientific applications and biomedical related research.
Liquid
Dye (330 to 1300 nm)
Used more widely in scientific applications.
Dye are energized by laser light to produce florescent light.

